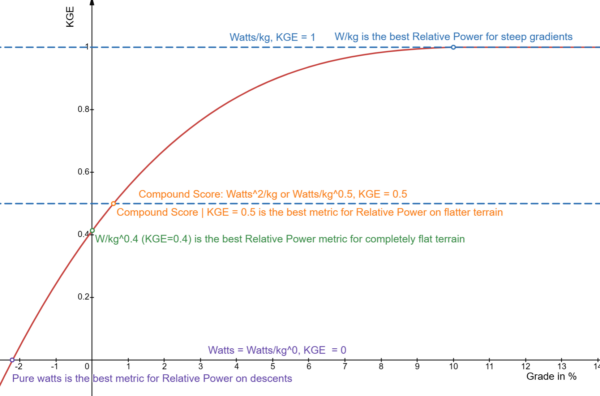
Kilogram Exponent (KGE) is the exponent used in the calculation of Relative Power. KGE is determined based on gradient of the terrain. In general, lower values indicate descending terrain whereas higher values indicate steeper grades.
Note that when KGE = 1, the exponent essentially means the same as Watts/KG whereas when KGE = 0, the exponent essentially means the same as Watts. In other words, the steeper the gradient, the more the weight of the rider comes into play. The flatter the terrain, the less weight impacts performance.
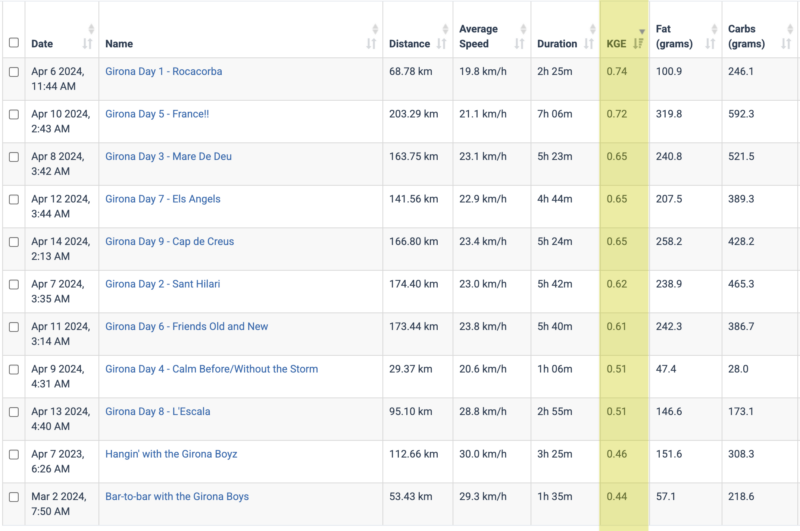
KGE in Relative Power Calculations
To use KGE to calculate Relative Power, you simply use KGE as the exponent using the athlete weight as the denominator and 75 kg as the numerator. For example, for a 90kg rider on flat ground (KGE = 0.42) at 300W, at 75kg rider would have to output 300*(75/90)^(0.42) = 278W or 22W less.
How Average KGE is Calculated
To calculate the average KGE for a given activity, Xert calculates a weighted average KGE based on the gradient and your power. So if you are pedaling easy down a hill, for example, these gradients have less influence on the KGE compared to those times when you are pedaling hard on a steep climb.
Calculating the Effect of Terrain on Power for a Given Rider Weight
Interestingly, the effect of a reduction of 1kg of body weight, for a given KGE (based on the gradient) at a given power can be calculated quite simply:
Increase in Relative Power per kg = watts/kg * KGE
As an example, reducing weight by 5kg where KGE = 0.5 at 375W for a 75kg rider, is 5*375/75*0.5 = 12.5W.