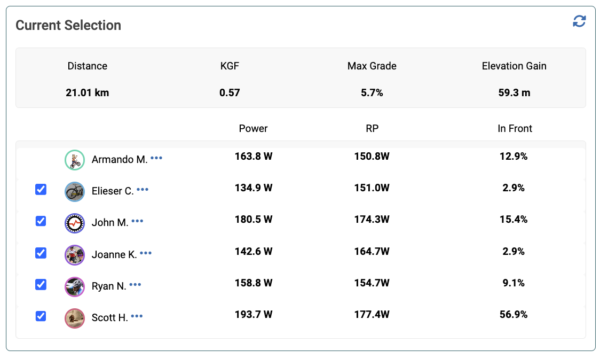
Xert Relative Power (XRP) quantifies how much power a typical male cyclist, weighing 75 kg, would need to produce in order to match the power of another rider, all else being equal*. The calculation used in Xert is:
Relative Power = Power * (75/mass)^kge
where mass is the weight in kilograms of the other rider and kge is the Kilogram Exponent (KGE). KGE is determined based on the gradient. The higher the gradient, the higher the KGE value.
For example, if a 65kg rider is generating 300W where the KGE is 0.7, the Relative Power is 300*(75/65)^0.7 = 332W. They would have a 32 watt advantage over a the 75kg rider.
* A rider can improve their Relative Power by reducing weight but also by improving other factors such as aerodynamics, rolling resistance, bike weight, and position on the bike.